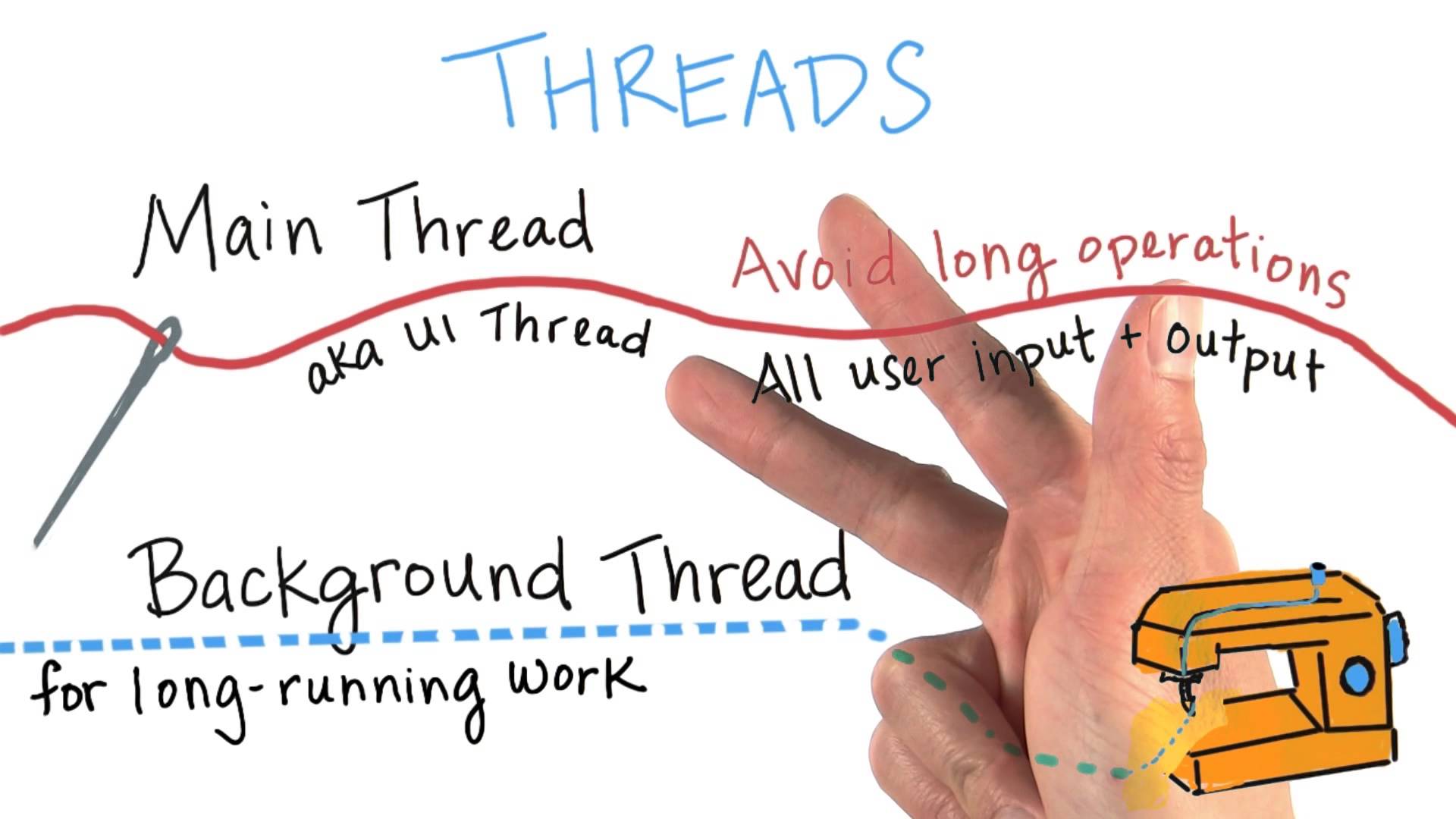
스레드
스레드
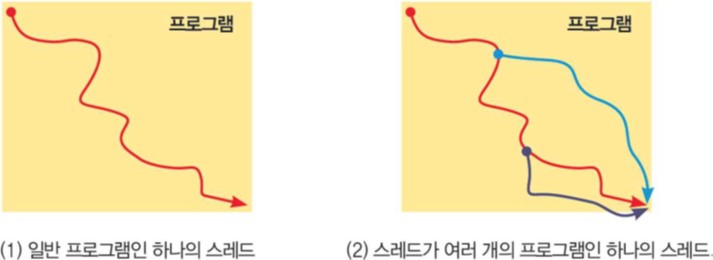
스레드(Thread)를 사전에서 찾아보면 ‘끈을 구성하는 실’이라는 뜻도 있다.
프로그래밍 용어의 스레드도 거기서 유래했고, 다음 그림이 보여주는 것처럼 스레드를 엮어서 하나의 프로그램을 조립할 수 있다.
멀티 스레드
멀티 스레드 란 이름 그대로의 복수의 스레드로 하나의 프로그램을 실행하는 기술이다. 왜 멀티 스레드를 사용하는 것 일까? 멀티 스레드를 사용하는 이유는 처리를 빠르게 하기 위함이다. 프로그램에서는 주로 논리적인 조작을 하면서 동시에 외부와 데이터를 주고받는 처리를 하게된다. 그런데 외부와의 연계에서 대기 시간이 발생하는 경우이가 있기 때문에 기다리는 시간 동안 다른일을 처리해두면 전체적인 처리 시간이 짧아지게 된다.
단, 멀티 스레드로 처리한다고 뭐든지 빨라지는 것은 아니다. 프로그램을 실행하는 컴퓨터의 CPU 코어 수가 적으면 병렬 처리 스레드를 그만큼 만들 수 없기 때문에 생각보다 빨라 지지 않는다. 그러므로 이용 상황을 잘 고려해서 꼭 멀티 스레드로 만들어야 할지 검토할 필요가 있다.
- MultiThreadSample.java
package thread;
/**
* 멀티스레드 샘플
*/
public class MultiThreadSample implements Runnable {
/** 출력 메시지 템플릿 */
private static final String MSG_TEMPLATE = "출력중입니다.[%s][%d회째]";
/** 스레드이름 */
private final String threadName;
public MultiThreadSample(String threadName) {
this.threadName = threadName;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(String.format(MSG_TEMPLATE, threadName, i));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MultiThreadSample runnable1 = new MultiThreadSample("thread1");
MultiThreadSample runnable2 = new MultiThreadSample("thread2");
MultiThreadSample runnable3 = new MultiThreadSample("thread3");
Thread thread1 = new Thread(runnable1);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(runnable2);
Thread thread3 = new Thread(runnable3);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.st,art();
}
}- 실행결과
출력중입니다.[thread2][1회째]
출력중입니다.[thread1][1회째]
출력중입니다.[thread2][2회째]
출력중입니다.[thread1][2회째]
... 생략 ...여러번 실행해보면 알 수 있지만 출력 순서가 매번 달라진ㄷ다. 그 이유는 처리가 동시에 실행되기 때문이다.
이번 예제에서는 멀티 스레드로 처리할 클래스에 Runnable 인터페이스를 구현했고, 스레드로 처리할 내용은 run 메서드에 기술했다.
Runnable 구현 클래스의 인스턴스를 바탕으로 Thread 인스턴스를 생성함으로써 스레드를 생성할 수 있습니다. 그리고 start 메서드로 스레드를 시작한ㄷ. 단순히 Runnable 인터페이스를 구현하고 run 메서드를 실행해서는 멀티 스레드로 실행되지 않는다.
더 복잡한 멀티 스레드 제어 방법
앞에서 설명한 멀티 스레드 작성 방법은 원시적인 형태라고 볼 수 있다. 멀티 스레드 프로그램이 어떤 것인지는 간략하게 알 수있지만, 실무에서 사용하기에는 문제가 있다.
좀 전의 예는 3개의 스레드만 만든 것이라서 문제가 없었다. 하지만, 스레드가 몇개 만들어질지 정해지지 않은 프로그램은 너무 많은 스레드가 한번에 실행될 가능성이 있다. 그 결과 동작 중인 컴퓨터의 메모리 자원을 다 써버려서 처리를 할 수 없게 만들 수 있다.
- 스레드 풀(Thread Pool)
자바에서는 스레드 풀이라는 기능을 제공한다. 스레드 풀이란 사용할 스레드를 제한된 수만큼 만들어두고 일정한 규칙에 따라 실행하는 기능으로, java.util.concurrent 패키지에서 제공한다.
- 스레드 풀 기능을 제공하는 인터페이스
| 인터페이스 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| ExecutorService | 스레드 수를 제한하는 등 일정한 제한 아래에서 멀티 스레드 처리를 실행하기 위한 인터페이스 |
| ScheduledExecutorService | 일정 시간 후에 시작하고 일정 제한 아래에서 멀티 스레드 처리를 실행하기 위한 인터페이스 |
- Executors 클래스의 주요 메서드
| 인터페이스 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| newSingleThreadExecutor | 싱글 스레드로 동작하는 ExecutorService의 인터페이스를 반환한다. |
| newFixedThreadPool | 지정한 최대 동시 실행 스레드 수로, ExecutorService의 인스턴스를 반환한다. |
| newScheduledThreadPool | 지정한 최대 동시 실행 스레드 수로, ScheduledExecutorService의 인스턴스를 반환한다. |
- ThreadPoolSample.java
package thread;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 스레드풀 샘플
*/
public class ThreadPoolSample implements Runnable {
/** 출력 메시지 템플릿 */
private static final String MSG_TEMPLATE = "출력중입니다. [%s][%d회째]";
/** 스레드 이름 */
private final String threadName;
public ThreadPoolSample(String threadName) {
this.threadName = threadName;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(String.format(MSG_TEMPLATE, threadName, i));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolSample runnable1 = new ThreadPoolSample("thread1");
ThreadPoolSample runnable2 = new ThreadPoolSample("thread2");
ThreadPoolSample runnable3 = new ThreadPoolSample("thread3");
// 스레드 동시 실행 수는 3스레드
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
executorService.execute(runnable1);
executorService.execute(runnable2);
executorService.execute(runnable3);
executorService.shutdown();
try {
if (!executorService.awaitTermination(5, TimeUnit.MINUTES)) {
// 타임아웃 후에도 아직 실행이 끝나지 않았다
executorService.shutdownNow();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// 종료 대기 시에 뭔가 오류가 발생했다
e.printStackTrace();
executorService.shutdownNow();
}
}
}스레드 풀을 newFixedThreadPool 메서드로 생상하고 있다. 이번에는 3개의 스레드를 동시에 실행하므로 인수(동시 실행 스레드 최대 수)에도 이 값을 지정한다. 또한, newFixedThreadPool 메서드의 인수를 1로 지정하면 동시 실행 수가 1이 되어 최초의 스레드부터 차례로 실행된다. 이 경우는 getSingleThreadExecutor 메서드로 ExecutorService의 인스턴스를 가져오는 것과 같다.
스레드는 execute 메서드로 시작하고 shutdown 메서드로 처리를 종료한다. 단, 그 자리에서 종료하는 것은 아니고, 실행 중인 스레드가 끝나야 비로소 종료 상태가 된다.
그래서 awaitTermination 메서드로 모든 스레드가 종료될 때까지 대기 상태로 둔다. 이 예제에서는 첫째 인수로 5를 지정하고, 둘째 인수로 TimeUnit.MINUTES를 지정했으므로 5분이 경과하면 타임아웃(종료)이 된다.
타임아웃이 되면 awaitTermination 메서드가 false를 반환한다. 예제에서는 타임아웃된 시점에 shutdownNow 메서드를 호출해서 실행 주인 메서드가 있어도 스레드를 강제로 종료한다.
단, 일반적인 어플리케이션에서는 (단순히 강제 종료하는 것이 아니라) 어떻게 대처할지 검토한 다음에 이상 시 처리를 기술할 필요가 있다.
또한 , InterruptedException__이 발생했을 떄의 처리가 예외 클래스의 __printstacktrace 메서드 호출과 shutdownNow 메서드 호출로 되어 있다. 이는 오류 정보를 출력하고 스레드를 강제 종료한다는 의미다. 이런 예외 처리에서도 타임 아웃과 마찬가지로 이상 처리를 검토할 필요가 있다.
Thread Safe
멀티 스레드로 동작하는 프로그램에서 개발자가 의도한 대로 동작하는 것을 가리킨다.
전혀 다른 일을 처리 할 때는 문제가 없겠으나, 공유자원을 참조할 때 개발자가 반드시 처리를 해줘야한다.
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class UnsafeSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
DateFormat unsafeDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
Calendar cal1 = Calendar.getInstance();
cal1.set(1989, Calendar.MARCH,10);
Date date1 = cal1.getTime();
Calendar cal2 = Calendar.getInstance();
cal2.set(2020, Calendar.JUNE,20);
Date date2 = cal2.getTime();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
try {
String result = unsafeDateFormat.format(date1);
System.out.println("Thread1 : " + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
break;
}
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
try {
String result = unsafeDateFormat.format(date2);
System.out.println("Thread2 : " + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
break;
}
}
});
System.out.println("스레드 세이프하지 않은 프로그램의 검증을 시작합니다.");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
콘솔을 실행해서 결과를 보면 Thread1은 1989/03/10이 100번, Thread2는 2020/06/20이 100번이 출력되어야 한다.
하지만 Thread1과 Thread2를 자세히 살펴보면, 출력 결과들이 섞여서 나온다. 왜일까?
내부적으로 굉장히 빠른 속도로 일을 처리하고 있을때, date1이 1989/03/10 찍고 있는데, 갑자기 date2도 SimpleDateFormat 클래스를 동시에 사용하기 때문에 발생한 것이다.
synchronized를 이용한 문제해결
- 하나의 객체를 여러 스레드에서 동시에 사용할 경우
- static으로 선언한 객체를 여러 스레드에서 동시에 사용할 경우
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class UnsafeSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
DateFormat unsafeDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
Calendar cal1 = Calendar.getInstance();
cal1.set(1989, Calendar.MARCH,10);
Date date1 = cal1.getTime();
Calendar cal2 = Calendar.getInstance();
cal2.set(2020, Calendar.JUNE,20);
Date date2 = cal2.getTime();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
try {
String result;
synchronized(unsafeDateFormat) {
result = unsafeDateFormat.format(date1);
}
System.out.println("Thread1 : " + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
break;
}
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
try {
String result;
synchronized(unsafeDateFormat) {
result = unsafeDateFormat.format(date2);
}
System.out.println("Thread2 : " + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
break;
}
}
});
System.out.println("스레드 세이프하지 않은 프로그램의 검증을 시작합니다.");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
출처
- 책 : 실무에서 바로 통하는 자바, 자바 성능 튜닝 이야기